
Geothermal Energy: Harnessing Earth's Heat for a Sustainable Future
Geothermal energy comes out as one of the most spirited contestants in the drive to find sustainable and reliable energy sources. As power is derived from heat inherent in the Earth, geothermal power provides a reliable and clean source of energy that is a notch higher than fossil energy sources. This article provides an overview of how geothermal energy works, the technological developments around it.
Understanding Geothermal Energy
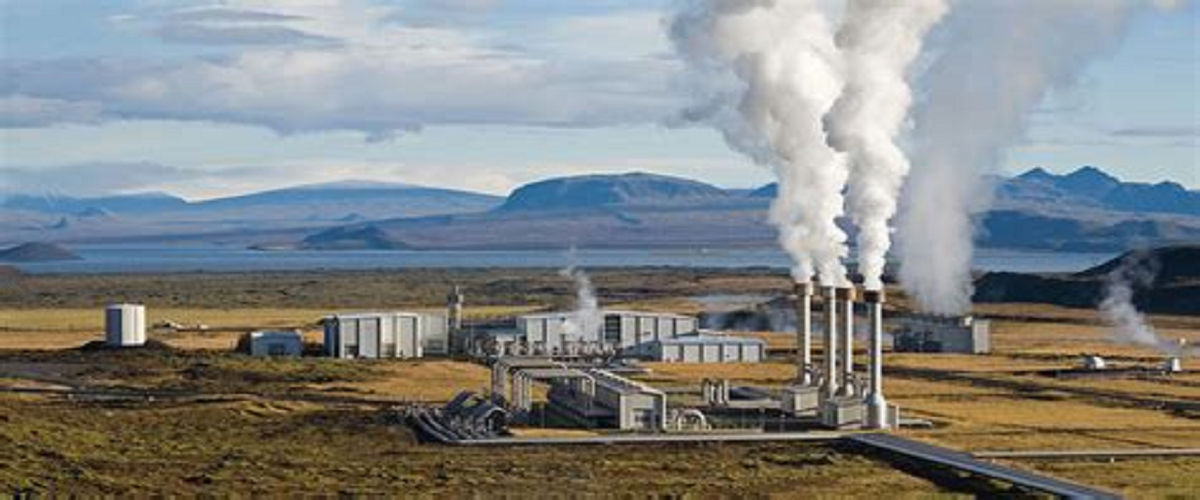
Geothermal energy is heat which is mined from inside the earth; most of it is derived from decaying Radioactive elements and the residual heat generated during earth formation. A form of thermal energy is hot water/steam found within the geosphere in the form of reservoirs within the earth’s crust for use in electricity generation and direct use.
Mechanisms of Geothermal Energy Extraction
Geothermal energy involves the exploration of drilled geothermal reservoirs from where steam and hot water can be tapped. This thermal fluid is then wasted to turbines for generation of electricity. The primary systems employed include:
- Dry Steam Plants: Exploit geothermal reservoir resources interactively to drive turbines.
- Flash Steam Plants: Pull high pressure hot water, flash this water and use steam so produced to turn turbine generators.
- Binary Cycle Plants: Uses hot water from the geothermal source as a first fluid to transfer heat to a second fluid that has a lower boiling point which vaporises and drives the turbines.
Global Developments in Geothermal Energy
Recent advancements underscore the expanding role of geothermal energy in the global energy matrix:
- Technological Innovations: The International Energy Agency (IEA) stresses that methods such as hydraulic fracturing, which were earlier used in oil and gas sector, can boost geothermal resources significantly. These methods can help develop more complex geothermal resources, and thus geothermal energy could produce up to 8% of the global electricity in 2050. (Financial Times)
- Corporate Investments: Google and Meta are just two big technology companies that are purchasing geothermal power for their data centers. For instance, Fervo Energy founded by CEO Tim Latimer is creating the pathway in improvement of drilling technologies for uninterrupted clean energy support where Google is powering its data centers with energy from Fervo.
(Time) - Regional Initiatives: In South East Asia, Indonesia and the Philippines have taken the initiative to develop geothermal energy in order to decrease the use of fossils. These nations are planning to expand geothermal capacity although high upfront costs and community opposition remain the major constraints. (AP News)
Advantages of Geothermal Energy
- Reliability: While solar and wind are intermittent sources of energy, geothermal form of energy provides a constant power supply without being variant by weather conditions.
- Environmental Sustainability: They release little, if any, greenhouse gases to the atmosphere than the fossil fuel-dependent plants; they reduce climate change impacts.
- Economic Development: Development of geothermal infrastructure from direct investments enhance the employment of citizens and establishment of supporting industries.
Challenges Facing Geothermal Energy Development
Despite its advantages, geothermal energy development encounters several obstacles:
- High Initial Costs: It is evident that the exploration and drilling phases are highly expensive; such costs discourage potential investors.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Like most infrastructure projects, there could be a number of procedural hindrances which include: long process of obtaining permits and numerous and relatively stringent regulatory frameworks which slow down the implementation process.
- Community Concerns: Local communities might have concerns in respect to the environment and land, meaning stakeholders’ involvement must be good.
Fundamental observation of geothermal energy reveals that it holds the key to achieving a sustainable energy future that is also resistant to shocks. The existing challenges may well be met by improving technologies and strategic alliance, in the given context, establishing the potential of this form of renewable energy to the full. The U.S. has embraced geothermal energy as a source of power and deservingly provides a successful example of how geothermal energy can complement national development and the conservation of the natural environment.


Comments